The NoSQL Revolution
by Teo Jing Yi
21 Mar 2019
What is NoSQL?

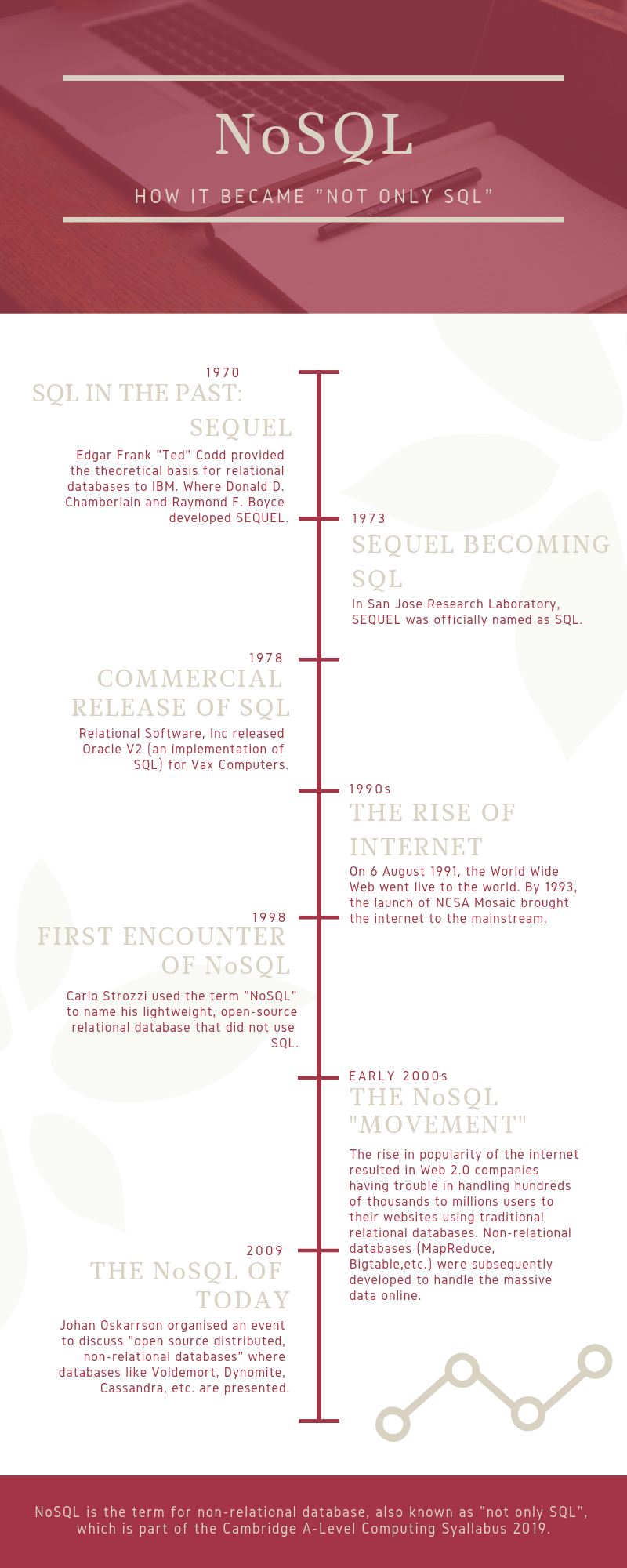
NoSQL stands for non-relational SQL and subsequently known as “Not Only SQL” as some NoSQL databases also supports SQL- like query language. It gained popularity after the traditional databases no longer can support the needs of Web 2.0 companies in the early 21st century. How exactly did NoSQL come about then? Scroll down to find out!
Types of NoSQL
NoSQL has 4 basic data models (databases) mainly, Document, Key-Value, Wide Column and Graph databases. We will now explore what each model do and how it benefits the user when using them.
Document:
Stores data in documents typically using a structure similar to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), XML (Extensive Markup Language), YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language), etc. and closely aligns with OOP (Object-Oriented Programming).
This speeds up developer productivity, simplifies data process and eliminates the need for expensive JOIN operations and complex, multi-record transactions otherwise needed in a traditional relational database.
Key-Value:
Stores data as a collection of key-value pairs, such that the value (data) can only be queried by the key.
It is computationally powerful as it is highly optimised due to the simplicity of the data access across patterns and opacity of the data itself. Many of the more complex NoSQL databases are built with Key-Value as their basis.
Wide Column:
Stores data in tables, rows and columns and unlike relational databases the names and formats of columns can differ from row to row. It can also be known as a 2D key-value store.
It works well in distributed systems, where enormous amount of data need to be stored and can be collected. Due to its architectural design, it can reduce query time and have massive scalability over and above the petabyte scale. ( 1 petabyte is approximately 1,000,000 gigabytes [GB] !)
Graph:
Uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges and properties to represent and store data. It treats the relationships between data on the same level of importance as the data itself.
In applications where traversing relationships are the core, like navigating social network connections, government, sports, etc. graph databases is an effective, constant time operation where you can quickly traverse millions of connections per second per core.
NoSQL vs SQL
After understanding roughly what NoSQL has to offer, you might be wondering what is it in NoSQL that makes it increasingly sought after in today’s world compared to relational databases like mySQL.
First things first, we would need to explore some programming terms.
ACID Paradigm (The Database Transaction Concept)
The ACID properties is intended to guarantee validity even in the events of errors, power failures, etc. Traditional SQL are made to be ACID compliant where:
-
Atomicity ensures transactions (made up of statements) are treated individually where it either passes as a whole or fails, when even a single statements fails to complete and leaves the rest of the database unchanged.
-
Consistency prevents database corruption as it ensures that a transaction can only bring the database from one valid state to another, according to all defined rules.
-
Isolation ensures concurrent execution of transactions leaves the database in the same state that would have been obtained if the transactions were executed sequentially.
-
Durability ensures the system’s ability to recover committed transaction updates if either the system or storage system fails.
Eventual Consistency (BASE)
- BA- Basically Available
- S - Soft state
- E - Eventual Consistency
Eventual Consistency is a consistency model that are used in distributed systems where the value for a specific data item will return the last updated value if no new updates are made to it.
CAP Theorem
CAP Theorem (also known as Brewer’s Theorem) states that no more than 2 out of 3 of the following properties – Consistency, Availability and Partition tolerance, can be provided at the same time by a distributed data store.
-
Consistency ensures that every read operation will return the most recent write value or the result of a later write operation.
-
Availability makes sure that every request received must result in a (non-error) response but the response is not guaranteed to be the most recent write value.
-
Partition tolerance ensures that the system still continues to operate despite losing arbitrarily many messages sent from one node to another.
After reading the terms, we can now venture into some of the differences between NoSQL from SQL databases.
Firstly, the processing and data handling speed. Since SQL is a table based database while NoSQL has 4 basic types of databases which in addition do not require the standard-predefined schema that SQL needs as it has dynamic schema for unstructured data which makes processing and handling real time online data to be much faster and fuss free.
Next, the scalability of the databases. SQL databases are vertically scalable meaning that in order to increase load, you have to increase the CPU, RAM, SSD, etc. on a single server whereas NoSQL being horizontally scalable, just requires you to add a few more servers on the database to handle the traffic. NoSQL databases would hence be significantly much more easier and effective than SQL databases to handle the online traffic.
So does it mean that NoSQL databases are definitely better than SQL databases?
Well, despite the above benefits, NoSQL still has its disadvantages due to the concepts that it offers and it is relatively new compared to SQL. Since NoSQL supports the CAP theorem and BASE whereas SQL offers the concept of ACID, ultimately SQL is the database with more consistent and accurate data values whereas NoSQL compromises parts of them for speed and flexibility in data processing. Furthermore, SQL databases (like SQL Servers) are also incorporating NoSQL features that promotes transparent tactics.
So does that mean that I have to sacrifice one property for another?
Absolutely not! Though NoSQL is a fairly new database system as compared to SQL, the demands in the market for much higher performing system and faster processing of real time data, technologies like Big Data Analytics, AI technology had probed for an accelerated improvement and breakthroughs in NoSQL technologies. Nowadays, NoSQL are adapting SQL-like features to promote data consistency and reliability as well as other useful and secure operations such as joins and customizable consistency, etc.
Now, enough talk about what NoSQL can do and start to get you moving, there are currently quite a number of well built and reliable NoSQL open-source databases for use. Examples of such are MongoDB for Document Oriented Database, Voldemort Database for Key-Value Database or even Google Bigtable and much more!
Ultimately, the choice of using SQL or NoSQL databases is entirely dependent on your needs and preferences. If you do not need to handle an enormously large amount of data, then SQL might be a better and more reliable choice to build your database on while on the other hand if you need to handle messy and extremely complicated data, you might want to venture into NoSQL databases.
So what are you waiting for, go open a new tab or window and start learning how databases (no matter SQL or NoSQL) will be able to help you in your careers, business or studies.
Stephen King, On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft
Amateurs sit and wait for inspiration, the rest of us just get up and go to work.”
Reference:
- M. (2018, June). Top 5 Considerations When Evaluating NoSQL Databases[PDF]. MongoDB.
- A Brief History of Non-Relational Databases. (2018, June 13). Retrieved January 15, 2019, from https://www.dataversity.net/a-brief-history-of-non-relational-databases/#